What is Hard Water and Why is it a Problem?
Water containing calcium and magnesium is hard water. Having hard water in your home can lead to numerous problems such as:
- Shorten the life of all water-using appliances.
- Increased hot water heating costs (up to 24% higher).
- Prevents clothing from being cleaned properly, no matter how much detergent is used.
- Cause deposits like limescale to cling to your glassware and dishware, causing a cloudy appearance
- Increase your chances of having soap scum and mineral build-up in your bathroom and kitchen, which means you’ll be spending more time cleaning and up to $90/month on cleaning supplies.
- An increased build-up of scale from mineral deposits diminishing water flow and pressure.
- Dries out your skin and hair.
Fortunately, a water softener can solve all these issues; the life of your appliances will be extended, your dishware will shine, and your clothing will be vibrant, clean, and last longer.
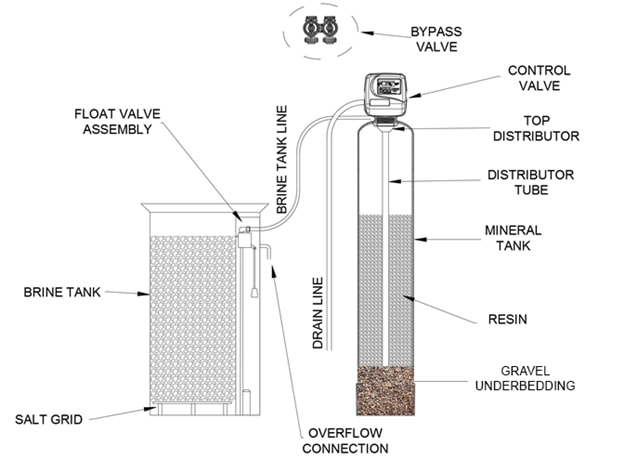
The Components of a Water Softener
A water softener consists of 5 main components:
Mineral Tank – The mineral tank has an internal distribution tube that will control the flow of water, delivering soft water or performing a regeneration. The under-bedding and softening resin is also located inside the mineral tank
Control Valve – This electronic demand control valve operates all cycles of the water softener regeneration process while monitoring and recording water usages, providing soft water, diagnostic information, and water usage history.
Brine Tank – Consists of a plastic container with a lid and brine well with safety float. Salt is stored inside this tank and, when mixed with water, produces the “brine” solution required to regenerate the water softener. The safety float allows the water to flow to and from the brine tank and protects the system from potential overflows.
Resin – Water softening occurs through cation Ion Exchange Resin. Negatively charged resin is called cation resin and attracts positive ions or cations. Resin beads are spherical, ranging from 0.5-1.0mm in diameter, and constructed of polystyrene.
Support Bed – The under-bedding in a water softener covers the lower distributor cone preventing and eliminating pressure drop after softening is achieved. It also acts as a filter to protect the resin, giving it a longer life.
The Water Softening Process
A water softener uses a process called ion exchange to remove hard water minerals, including calcium and magnesium, from your water supply.
As hard water enters the water softener, it flows into the mineral tank, passing through the negatively charged cation exchange resin bed. When positively charged hard water minerals (calcium and magnesium) pass through, they stick to the resin bed, leaving soft water to flow to the under bedding and up through the distributor, providing soft water to your household.
When the water softener has exhausted its capacity, it will add water to the brine tank before regeneration. This allows the water softening salt to be turned into a liquid brine. The liquid brine is used during regeneration to clean the cation resin bed and sends chlorides with the calcium and magnesium to drain. The water softener then goes back into service, and the cycle starts again.
What Does a Water Softener Remove?
A water softener removes hard water minerals like magnesium and calcium, which cause problems around your home like staining and mineral build-up in your kitchen and bathroom, cloudy glassware, increased energy costs, and dull, stiff clothing, to name a few.
The system also removes dissolved iron and manganese from your water. Despite your water looking clear, dissolved iron can leave red stains on your toilet, sink, and bathtub, while manganese can leave black stains and a metallic taste in your water. All these aesthetic impurities are removed with a water softener.
How Water Softener Regeneration Works
After a specific, metered amount of water passes through the water softener, the resin in the system becomes exhausted, containing only calcium and magnesium. At this point, the resin bed needs to be flushed free of hard water minerals, which is done through ion exchange.
- The Backwash Cycle is the first cycle of regeneration. The water flows into the control valve, down the riser tube, and out through the collector. Water then flows upward through the resin, expanding it out the top of the tank to the drain. The expansion mixes up the resin and removes any turbidity and other contaminants, which get filtered out during the service cycle.
- The Brine Draw/Slow Rinse is the second cycle of the regeneration process. Brine solution is drawn into the valve with the injector and enters the top of the softener tank. The brine solution then flows down through the resin, exchanging the sodium portion of the sodium chloride for the hardness ions collected on and in the resin bed. This cycle continues until all the liquid brine has been drawn into the water softener. A slow rinse begins when the ball in the safety float air-check at the bottom of the brine tank seats. Water continues to flow through the injector into the top of the water softener and down through the resin at a controlled flow rate. The excess brine and the remainder of the hardness is rinsed off the resin during this cycle.
- The second backwash third cycle of the regeneration process will again cycle water flow into the valve, down the riser tube, and out through the collector. The water then flows up through the resin, expanding it and out the top of the tank to the drain. This backwash mixes the regenerated resin bed, distributing highly regenerated resin throughout the bed and removing any access sodium chloride to drain.
- The fourth cycle of the regeneration process is the fast rinse, where water enters the softener tank and flows down through the resin at an increased flow rate before being sent to drain. This high flow rate compacts the resin bed and rinses out the last of the brine and hardness, achieving the resin bed back to the service position and delivering soft water.
- The Refill Cycle is the last step and cycle to the regeneration process where soft water is directed back to the brine tank at a flow rate of 0.5gpm. Each gallon of water will dissolve three pounds of salt. The water lifts the air-check ball off the seat of the brine float assembly when filling soft water into the salt tank. The amount of water is timed through the control valve based on the capacity and salt setting of the water softener. Water softeners can use between 3-15lbs of salt per regeneration.
Example: Salt setting on softener 6lbs of salt
The brine fill time will be 3min @ 0.5gpm = 3 gallons of water which will dissolve 6lbs of salt. After the refill cycle is complete, the softener control valve returns to the service position.
The Best Way to Soften Water
The best way to soften water is to use a water softener. A water softener removes hard water minerals from your water supply through the ion exchange process. Calcium and magnesium (hard water minerals) are stripped from the water as it flows through the water softener resin bed, making water soft as it flows into your home. When you install a water softener, faucets and showers in your home will have soft water from your kitchen to your bathroom.
How Long Does a Water Softener Last?
Water softeners typically last up to 25 years with proper maintenance when utilizing the best components in the water treatment industry.
What Water Softener Size Should I buy?
To size a water softener correctly, we need to do the following calculation:
For each person in your household, add 50 gallons/day. If you have a dishwasher, consider it a person in this calculation. For example, if you have 4 people in your household and a dishwasher, multiply 50 gallons/day x 5. This gives you your total gallons/day. You then multiply your total gallons/day x the hardness of your water to get your grains per day. Finally, take your grains/day and multiply it by 5 to get your water softener size.
50 gallons/day x people in your household = Total Gallons/Day
Total Gallons/Day x water hardness = Total Grains/Day
Total Grains/Day x 5 = Water Softener Total Capacity
How Do I Use My Water Softener Correctly?
After installing a water softener, there is some simple programming required before use, as the water softener control valve will be pre-programmed by the manufacturer and needs to be adjusted to your households’ specific needs.
First, you must change the water hardness on your water softener control valve to reflect the water hardness of your water supply. You should add 5 grains to the hardness setting for every 1 ppm of dissolved ferrous iron or manganese.
Second, you must set the time on your control valve.
Lastly, in the event your water softener hasn’t regenerated, the manufacturer has set an override so the system will regenerate automatically after 14 days to protect the system. You can adjust the override from 1-28 days.
After this simple setup, the water softener is fully automatic, and no further programming changes are required. The only thing you need to do is add water softening salt to the brine tank, relax and enjoy!
What Kind of Salt Do I Use For My Water Softener?
You can use pellet, solar, or rock water softening salt for your water softener. For the best operation of your water softener, we recommend you use the purest water softening salt available (pellets or solar).
If you use rock salt your liquid brine in the salt tank can look grey in colour as there is a small amount of dirt in this type of salt. The dirt in the salt can plug the injector in your water softener during a regeneration and when this happens the liquid brine made in the regeneration process will not be drawn into the softener mineral tank to regenerate the resin resulting in no soft water. A good indication of a plugged injector is a constant high level of water in your salt tank.
Though rock water softening salt is usually the more inexpensive option, we recommend you only use high purity water softening salt to prevent issues like a salt bridge from occurring. When filling your brine salt storage tank with salt do not overfill only fill the salt tank ½ full at any point of time as most pure pellet salts use an adhesive glue to bind these pellets together and with excessive extra weight on the salt at the bottom can possibly not dissolve properly, much and cause issues like a salt bridge or mushed non-dissolved salt plugging the bottom slots of the brine well of the safety float.
How Do I Know if I Need a Water Softener?
The best way to determine if you have hard water is to schedule a free water test. You can also look around your home for the telltale signs of hard water:
- Stiff, dull clothing, even after having just been washed
- Reduced water flow and pressure from showerheads and faucets
- Staining and mineral build-up around faucets, handles, glass shower doors, and handles
- Dry skin and hair after a shower
- Cloudy glassware that never looks clean
- Soap scum build-up in your bathroom and kitchen
- Increased energy costs from build-up in your hot water tank/tankless heater



